Avec l’arrivée du protocole SMB 3.0, partie intégrante de Windows 8 et Windows Server 2012, voici un tour d’horizon sur l’évolution de SMB et la compatibilité entre les différentes versions.
Versions
- CIFS – Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
- SMB 1.0 – Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 et Windows Server 2003 R2
- SMB 2.0 – Windows Vista (SP1) et Windows Server 2008
- SMB 2.1 – Windows 7 et Windows Server 2008 R2
- SMB 3.0 (ou SMB2.2) – Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
L’historique
- De SMB 1.0 à SMB 2.0 – Redesign majeur
- Increased file sharing scalability
- Performances accrues
- Request compounding
- Asynchronous operations
- Larger reads/writes
- Plus sécurisé et robuste
- Small command set
- Signing now uses HMAC SHA-256 instead of MD5
- SMB2 durability
- De SMB 2.0 à SMB 2.1
- File leasing improvements
- Support MTU large
- BranchCache
- From SMB 2.1 to SMB 3.0
- Disponibilité
- SMB Transparent Failover
- SMB Witness
- SMB Multichannel
- Performances
- SMB Scale-Out
- SMB Direct (SMB 3.0 over RDMA)
- SMB Multichannel
- Directory Leasing
- BrachCache V2
- Sauvegarde
- VSS pour Remote File Shares
- Sécurité
- Encryption SMB
- o Management
- SMB PowerShell
- Compteurs de Performances améliorés
- Evénements améliorés
- Disponibilité
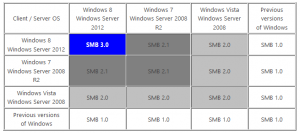
Correspondance client/serveur
Vérifier la version SMB employée
Il convient de lancer la commande suivante: